Brain Hemorrhage
What is a brain hemorrhage? Causes, symptoms, and treatment of brain hemorrhage...
A brain hemorrhage (aneurysm) is a condition characterized by symptoms such as sudden and severe headache, nausea, vomiting, difficulty speaking, and dizziness. So, what is a brain hemorrhage?
A brain hemorrhage is a serious condition in which the skull and brain are damaged due to a sudden increase in blood flow to the brain. If not treated early, it can lead to serious health problems. Now, let's explain the causes, symptoms, and treatment of brain hemorrhages.
WHAT IS BRAIN HEMORRHAGE?
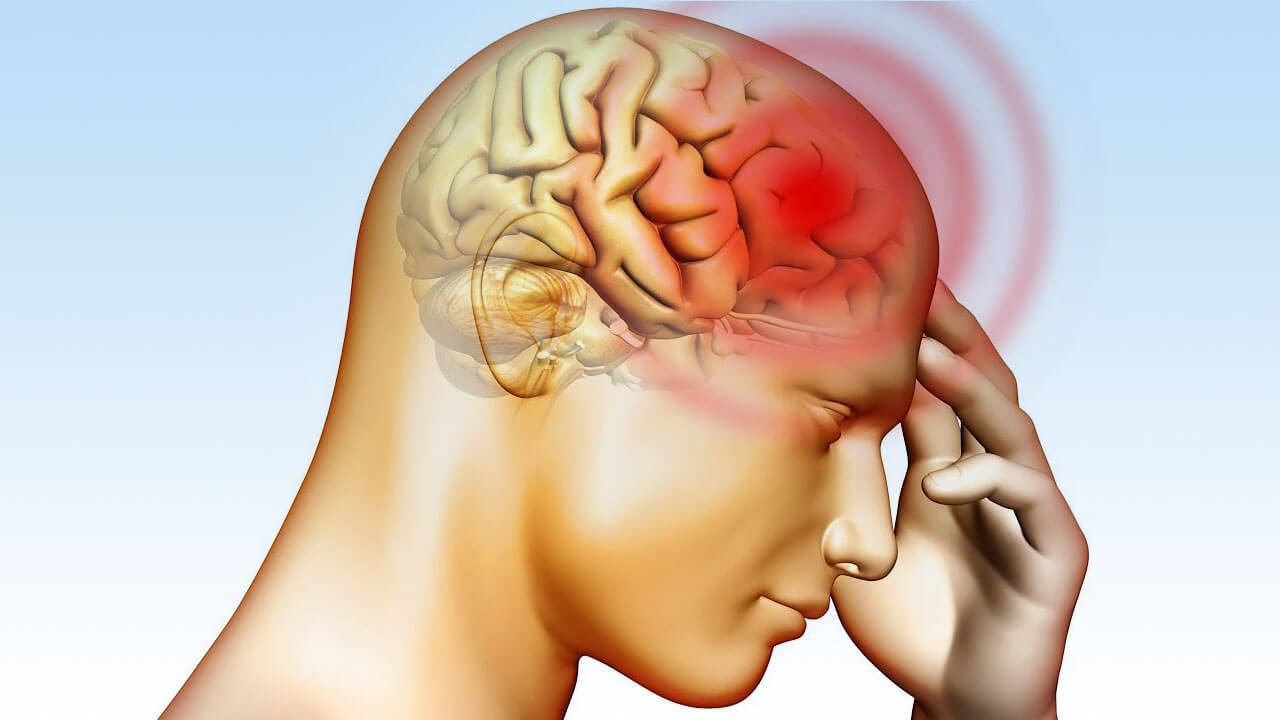
A brain hemorrhage is a condition that occurs when the walls of the blood vessels that feed the brain rupture, causing blood to leak into the brain and destroy the brain tissue.Brain hemorrhages are often labeled according to where they occur in the brain. Generally, bleeding anywhere within the skull is called an intracranial hemorrhage. Bleeding within the brain is known as an intracerebral hemorrhage. Bleeding can also occur between the brain and the brain tissue itself, called a subarachnoid hemorrhage. If a blood clot forms between the skull and the brain, it is called a subdural or epidural hematoma, depending on whether it is above or below the brain's tough covering (dura). Subdural and epidural hematomas occur as a result of trauma or after a fall.
Causes of Brain Hemorrhage
There are several risk factors and causes of brain hemorrhage. The most common are:– Head trauma
Injury is the most common cause of bleeding in the brain for people younger than 50.
Injury is the most common cause of bleeding in the brain for people younger than 50.
– High blood pressure
This chronic condition can weaken blood vessel walls over time. Untreated high blood pressure is a major cause of brain hemorrhages.
This chronic condition can weaken blood vessel walls over time. Untreated high blood pressure is a major cause of brain hemorrhages.
– Aneurysm
This is a weakening of the wall of a swollen blood vessel. It can rupture, allowing blood to leak into the brain, which can lead to a stroke.
This is a weakening of the wall of a swollen blood vessel. It can rupture, allowing blood to leak into the brain, which can lead to a stroke.
– Blood vessel abnormalities (Arteriovenous malformations)
Weaknesses in the blood vessels in and around the brain may be present at birth and are only diagnosed if symptoms develop.
Weaknesses in the blood vessels in and around the brain may be present at birth and are only diagnosed if symptoms develop.
– Amyloid angiopathy
This is an abnormality of the blood vessel walls that sometimes occurs with aging and high blood pressure. It can cause very small, unnoticeable bleeding before it becomes a major cause.
This is an abnormality of the blood vessel walls that sometimes occurs with aging and high blood pressure. It can cause very small, unnoticeable bleeding before it becomes a major cause.
– Blood or bleeding disorders
Hemophilia and sickle cell anemia can both contribute to decreased blood platelets.
Hemophilia and sickle cell anemia can both contribute to decreased blood platelets.
– Liver disease
– Brain tumor
– Use of alcohol, drugs, etc.
– Brain tumor
– Use of alcohol, drugs, etc.
BRAIN HEMORRHAGE SYMPTOMS
A brain hemorrhage can cause a variety of different symptoms. These symptoms may include sudden tingling, weakness, numbness, or paralysis in the face, arm, or leg. This is likely to occur on only one side of the body.Other symptoms of a brain hemorrhage include:
– Sudden, severe headache
– Difficulty swallowing
– Vision problems
– Loss of balance or coordination
– Confusion or difficulty understanding
– Difficulty speaking
– Drowsiness or unconsciousness
– Seizures
– Sudden, severe headache
– Difficulty swallowing
– Vision problems
– Loss of balance or coordination
– Confusion or difficulty understanding
– Difficulty speaking
– Drowsiness or unconsciousness
– Seizures
BRAIN HEMORRHAGE TREATMENT
Patients with bleeding within the brain must be monitored very closely. Early treatment includes stabilizing blood pressure and breathing. A breathing assistant (ventilator) may be required to ensure adequate oxygen delivery to the brain and other organs. Intravenous access is required so the patient can receive fluids and medications, especially if the person is unconscious. Sometimes, special monitoring of heart rhythms, blood oxygen levels, or intracranial pressure is necessary.Once a person is stabilized, a decision is made about how to stop the bleeding. The decision to perform surgery depends on the extent and location of the bleeding. Not everyone with an intracranial hemorrhage requires surgery.
Various medications may be used to reduce swelling around the bleeding area, maintain optimal blood pressure, and prevent seizures. Pain medication may be necessary if the patient is awake.
